Worlds Top 10 Most Popular & Highly Developed Countries

Colorful Norway (Photo Credit: Edward Dalmulder
/ CC BY 2.0)
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a sovereign and unitary monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula plus Jan Mayen and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard. The Antarctic Peter I Island and the sub-Antarctic Bouvet Island are dependent territories and thus not considered part of the Kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land. Until 1814, the Kingdom included the Faroe Islands, Greenland, and Iceland.
The country maintains a combination of market economy and a Nordic welfare model with universal health care and a comprehensive social security system. Norway has extensive reserves of petroleum, natural gas, minerals, lumber, seafood, fresh water, and hydropower. The petroleum industry accounts for around a quarter of the country’s gross domestic product. The country has the fourth-highest per capita income in the world on the World Bank and IMF lists, as well as ninth-highest on a more comprehensive CIA list. On a per-capita basis, it is the world’s largest producer of oil and natural gas outside the Middle East.
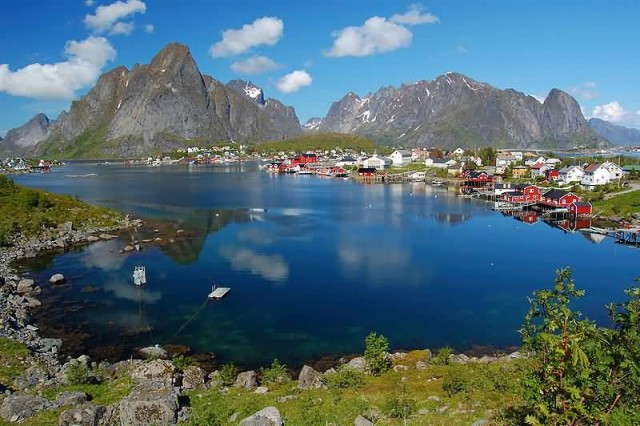

Norway Reine Lofoten (Photo Credit: melenama / CC BY-SA 2.0)
From 2001 to 2006, and then again from 2009 to 2014, Norway had the highest Human Development Index ranking in the world. Norway has also topped the Legatum Prosperity Index for the last five years. Norway is considered to be one of the most developed democracies and states of justice in the world. From 1814, c. 45% of men had the right to vote, whereas England had c. 20%, Sweden c. 5%, and Belgium c. 1.15% . Since 2010, Norway has been classified as the world’s most democratic country by the Democracy Index.
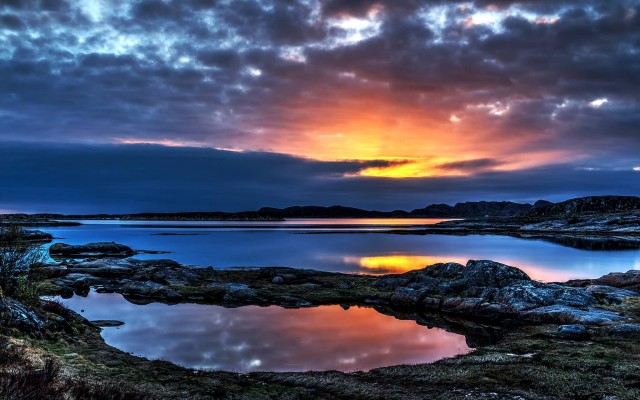

Beautiful Norway (Photo Credit: Nils Tamlag
/ CC BY 2.0)
Australia
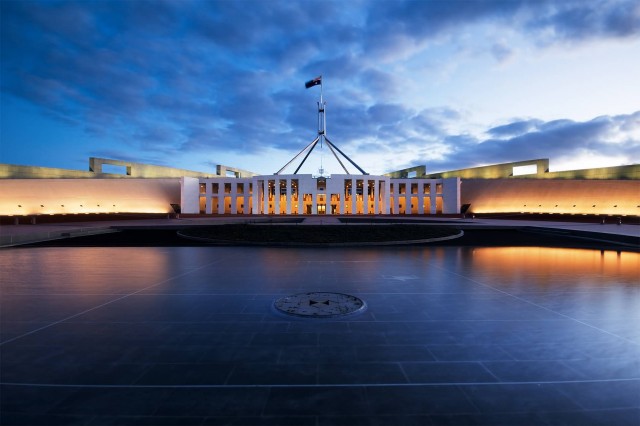

Parliament House Canberra Ns (Photo Credit: JJ Harrison / CC BY-SA 3.0)
Australia officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is an Oceanian country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. It is the world’s sixth-largest country by total area. Neighbouring countries include Indonesia, East Timor and Papua New Guinea to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. Australia is a developed country and one of the wealthiest in the world, with the world’s 12th-largest economy.
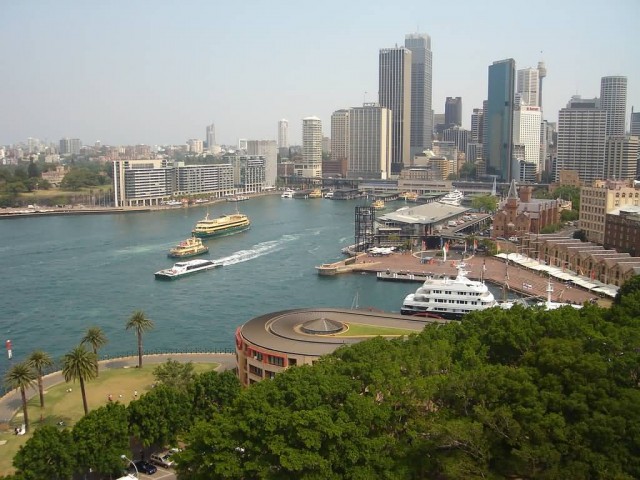

Sydney Harbour Australia (Photo Credit: Kevin Gibbons
/ CC BY 2.0)
In 2014 Australia had the world’s fifth-highest per capita income. Australia’s military expenditure is the world’s 13th-largest. With the second-highest human development index globally, Australia ranks highly in many international comparisons of national performance, such as quality of life, health, education, economic freedom, and the protection of civil liberties and political rights. Australia is a member of the United Nations, G20, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, World Trade Organization, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, and the Pacific Islands Forum.
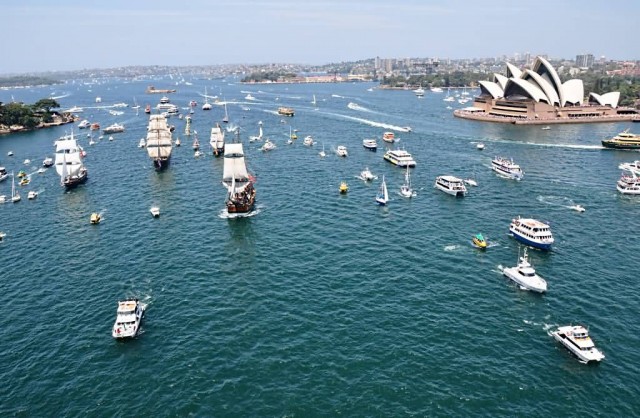

Australia (Photo Credit: Travis Simon / CC BY 2.0)
Netherlands

Netherlands (Photo Credit: Maarten Takens / CC BY-SA 2.0)
The Netherlands is the main constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It is a small, densely populated country, located in Western Europe and with three island territories in the Caribbean. The European part of the Netherlands borders Germany to the east, Belgium to the south, and the North Sea to the northwest, sharing maritime borders with Belgium, the United Kingdom and Germany. The largest and most important cities in the Netherlands are Amsterdam, The Hague and Rotterdam.
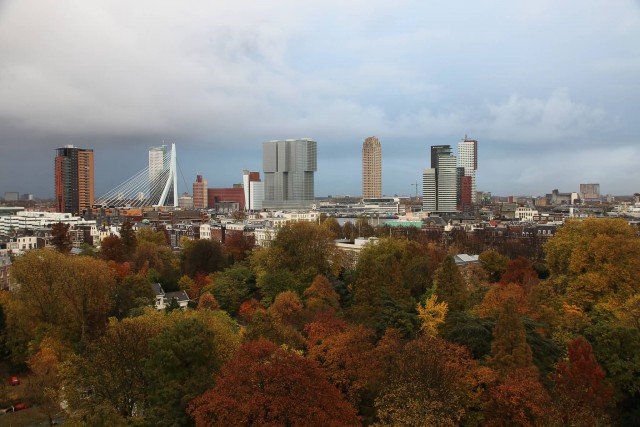

Rotterdam (Photo Credit: Rick Ligthelm / CC BY 2.0)
Amsterdam is the country’s capital, while The Hague holds the Dutch seat of government and parliament. The port of Rotterdam is the largest port in Europe – as large as the next three largest combined. The Netherlands has a market-based mixed economy, ranking 17th of 177 countries according to the Index of Economic Freedom. It had the thirteenth-highest per capita income in the world in 2013 according to the International Monetary Fund. In 2013, the United Nations World Happiness Report ranked the Netherlands as the fourth happiest country in the world, reflecting its high quality of life.

Amsterdam (Photo Credit: josef.stuefer
/ CC BY 2.0)
United States of America

Manhattan Bridge (Photo Credit: Scott Hudson / CC BY 2.0)
The United States of America, commonly referred to as the United States or America, is a federal republic consisting of 50 states and a federal district. The 48 contiguous states and Washington, D.C., are in central North America between Canada and Mexico. The state of Alaska is located in the northwestern part of North America and the state of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific. The country also has five populated and numerous unpopulated territories in the Pacific and the Caribbean.
At 3.8 million square miles and with over 320 million people, the United States is the world’s fourth-largest country by total area and third most populous. It is one of the world’s most ethnically diverse and multicultural nations, the product of large-scale immigration from many countries. The geography and climate of the United States are also extremely diverse, and the country is home to a wide variety of wildlife.
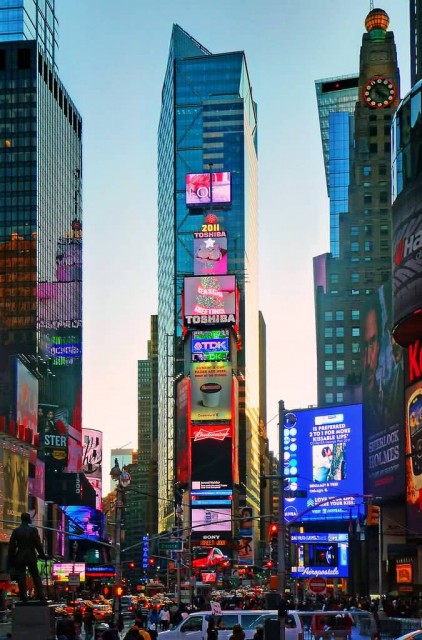

Times Square Dusk (Photo Credit: George Rex / CC BY-SA 2.0)
The United States is a developed country and has the world’s largest economy by nominal and real GDP, benefiting from an abundance of natural resources and high worker productivity. While the U.S. economy is considered post-industrial, the country continues to be one of the world’s largest manufacturers. Accounting for 34% of global military spending and 23% of world GDP, it is the world’s foremost economic and military power, a prominent political and cultural force, and a leader in scientific research and technological innovations.

Stand Taller (Photo Credit: Always Shooting / CC BY 2.0)
New Zealand

Looking Down On Downtown Buildings (Photo Credit: Lester Blair
/ CC BY-SA 2.0)
New Zealand is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses that of the North Island, or Te Ika-a-Māui, and the South Island, or Te Waipounamu and numerous smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long isolation, New Zealand developed a distinctive biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life.
The country’s varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand’s capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland. Nationally, legislative authority is vested in an elected, unicameral Parliament, while executive political power is exercised by the Cabinet, led by the Prime Minister, who is currently John Key. Queen Elizabeth II is the country’s head of state and is represented by a Governor-General.

Car Park Building (Photo Credit: Lester Blair / CC BY-SA 2.0)
In addition, New Zealand is organised into 11 regional councils and 67 territorial authorities for local government purposes. The Realm of New Zealand also includes Tokelau, the Cook Islands and Niue, and the Ross Dependency, which is New Zealand’s territorial claim in Antarctica. New Zealand is a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Pacific Islands Forum and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation.
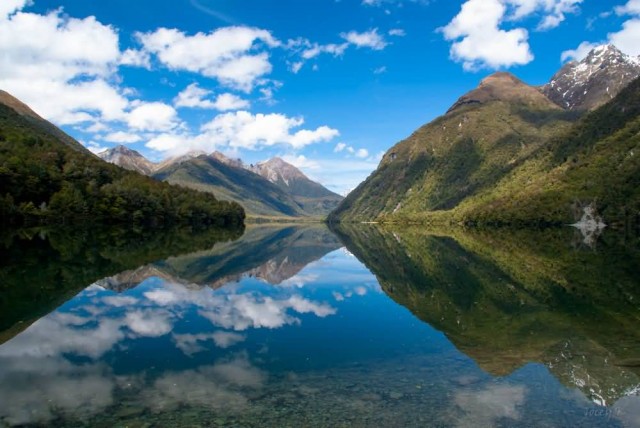

Lake Gunn (Photo Credit: Jocelyn Kinghorn
/ CC BY-SA 2.0)
Canada
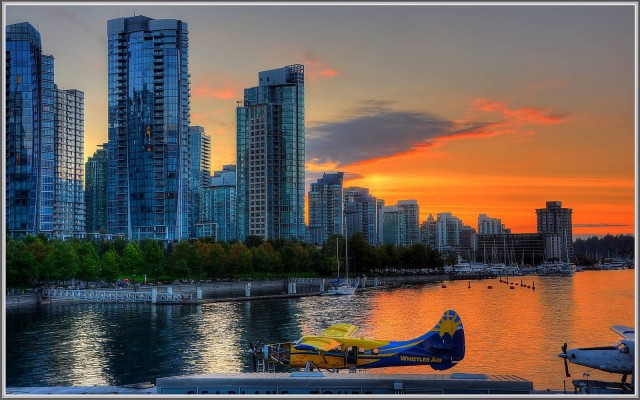

Coal Harbor Sunset (Photo Credit: tdlucas5000 / CC BY 2.0)
Canada is a country, consisting of ten provinces and three territories, in the northern part of the continent of North America. It extends from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres in total, making it the world’s second-largest country by total area and the fourth-largest country by land area. Canada’s common border with the United States forms the world’s longest land border. Canada is a developed country and one of the wealthiest in the world, with the tenth highest nominal per capita income globally, and the eighth highest ranking in the Human Development Index.
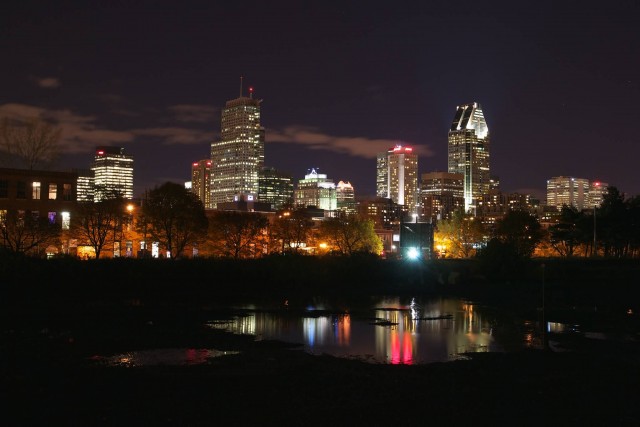

Montreal Shining (Photo Credit: Clément Belleudy / CC BY-SA 2.0)
It ranks among the highest in international measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life, economic freedom, and education. Canada is a Commonwealth Realm member of the Commonwealth of Nations, and is furthermore part of several major international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings, including the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the G8, the Group of Ten, the G20, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum.
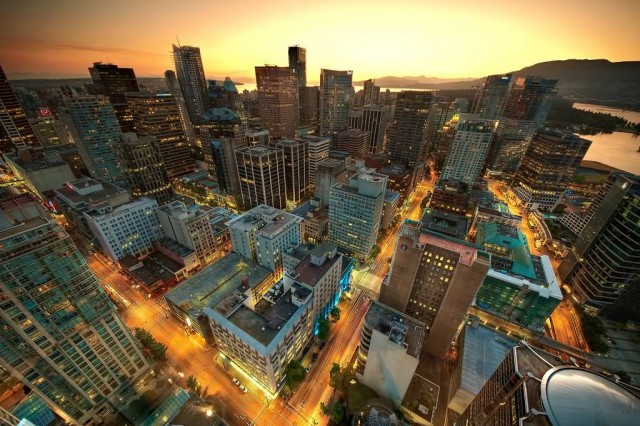

Downtown Vancouver Sunset (Photo Credit: Magnus Larsson / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Ireland
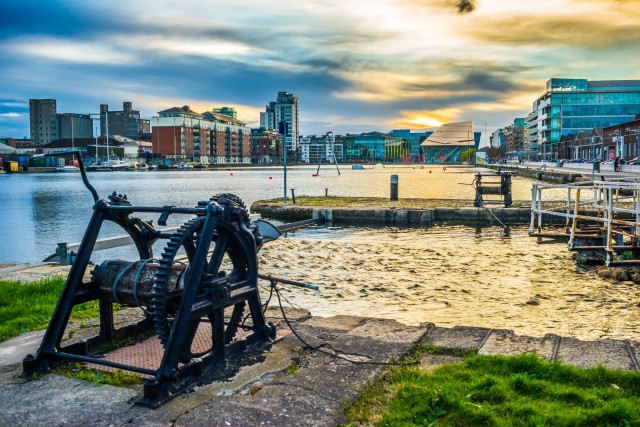

Sunset In Grand Canal (Photo Credit: Giuseppe Milo / CC BY 2.0)
Ireland is an island in the North Atlantic separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George’s Channel. It is the second-largest island of the British Isles after Great Britain, the third-largest in Europe and the twentieth-largest on Earth.
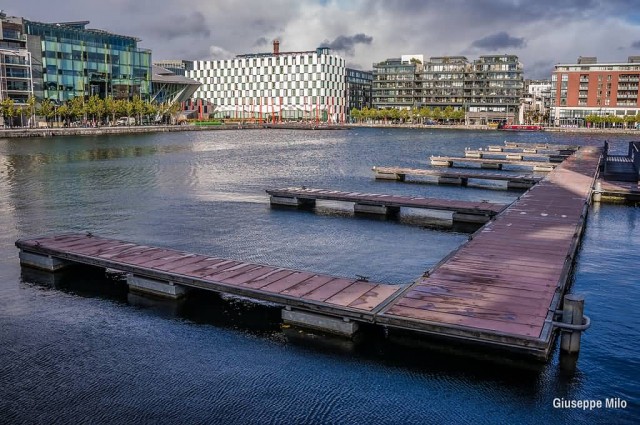

Grand Canal Dublin Ireland (Photo Credit: Giuseppe Milo / CC BY 2.0)
Irish culture has had a significant influence on other cultures, especially in the fields of literature and, to a lesser degree, science and education. Alongside mainstream Western culture, a strong indigenous culture exists, as expressed for example through Gaelic games, Irish music, and the Irish language. The culture of the island has also many features shared with Great Britain, including the English language, and sports such as association football, rugby, horse racing, and golf.
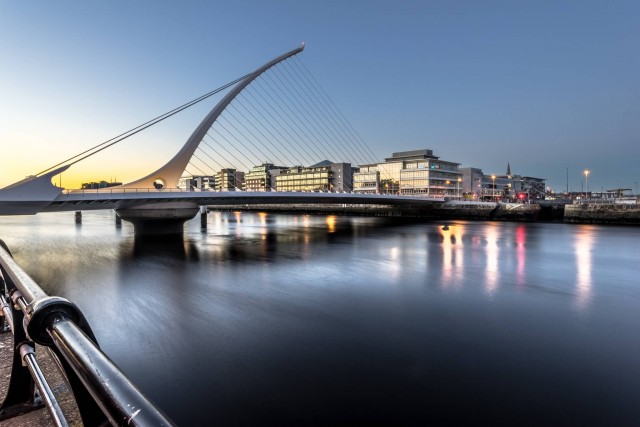

Samuel Beckett Bridge At Sunset (Photo Credit: Giuseppe Milo / CC BY 2.0)
Liechtenstein

Euro Road Trip (Photo Credit: Kyle Taylor / CC BY 2.0)
Liechtenstein, officially the Principality of Liechtenstein, is a doubly landlocked German-speaking microstate in Central Europe. It is a constitutional monarchy with the rank of principality, headed by the Prince of Liechtenstein. Economically, Liechtenstein has the highest gross domestic product per person in the world when adjusted by purchasing power parity.

Liechtenstein (Photo Credit: thisisbossi / CC BY-SA 2.0)
It is also the 2nd richest country in the world, after Qatar, and has one of the lowest unemployment rates at 1.5%. An alpine country, Liechtenstein is mainly mountainous, making it a winter sports destination. Many cultivated fields and small farms are found both in the south and north. The country has a strong financial sector centered in Vaduz, and has been identified as a tax haven. Liechtenstein is a member of the European Free Trade Association, and, while not a member of the European Union, the country participates in both the Schengen Area and European Economic Area. It also has a customs union and a monetary union with Switzerland.
Germany
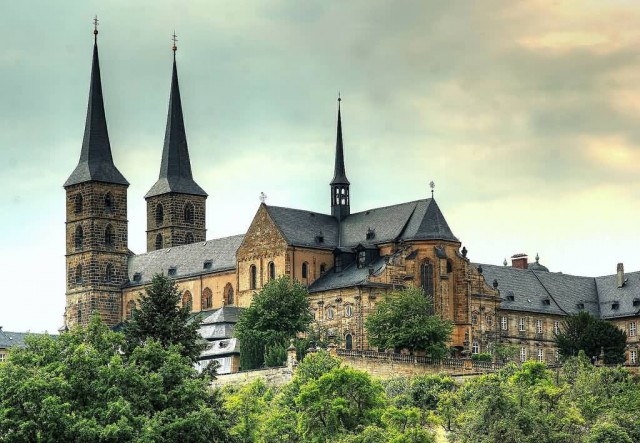

Bamberg germany (Photo Credit: Thomas Depenbusch
/ CC BY 2.0)
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It includes 16 constituent states and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. With 80.7 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is the second most popular migration destination in the world.
In the 21st century, Germany is a great power and has the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP and the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world’s third-largest exporter and importer of goods. It is a developed country with a very high standard of living, and it maintains a comprehensive social security and a universal health care system.

Germany (Photo Credit: Thomas Depenbusch / CC BY 2.0)
Germany was a founding member of the European Communities in 1957, which became the European Union in 1993. It is part of the Schengen Area, and became a co-founder of the Eurozone in 1999. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G8, the G20, and the OECD. Known for its rich cultural history Germany has been continuously the home of influential artists, philosophers, musicians, entrepreneurs, scientists and inventors.
Sweden

Stockholm Riddarholmen (Photo Credit: Olof Senestam
/ CC BY 2.0)
Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres, Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of over 9.7 million. Sweden subsequently has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre, with the highest concentration in the southern half of the country.
Approximately 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the geographical area of Fennoscandia. Today, Sweden is a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy, with the Monarch as the head of state. The capital city is Stockholm, which is also the most populous city in the country. Legislative power is vested in the 349-member unicameral Riksdag. Executive power is exercised by the Government, chaired by the Prime Minister.
Sweden is a unitary state, currently divided into 21 counties and 290 municipalities. Sweden maintains a Nordic social welfare system that provides universal health care and tertiary education for its citizens. It has the world’s eighth-highest per capita income and ranks highly in numerous metrics of national performance, including quality of life, health, education, protection of civil liberties, economic competitiveness, equality, prosperity and human development.

Sergels Torg Stockholm Sweden (Photo Credit: Giuseppe Milo
/ CC BY 2.0)