10 Most Famous Churches In The World

Sagrada Familia (Photo Credit: Bernard Gagnon / CC BY-SA 3.0)
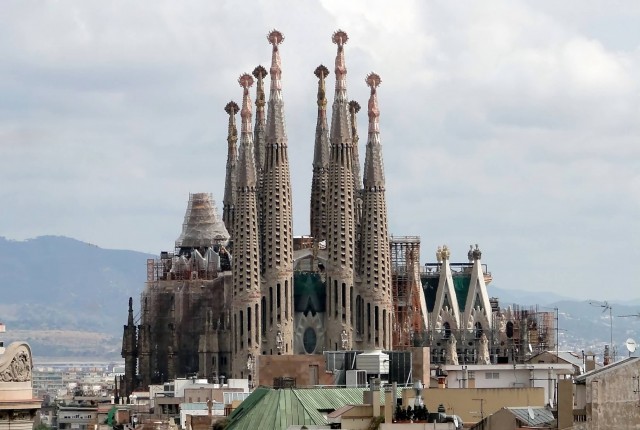
Sagrada Familia, Barcelona
The Basílica i Temple Expiatori de la Sagrada Família, is a large Roman Catholic church in Barcelona, Catalonia, designed by Catalan architect Antoni Gaudí (1852–1926). Although incomplete, the church is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and in November 2010 Pope Benedict XVI consecrated and proclaimed it a minor basilica, as distinct from a cathedral which must be the seat of a bishop.
Construction of Sagrada Família had commenced in 1882 and Gaudí became involved in 1883, taking over the project and transforming it with his architectural and engineering style, combining Gothic and curvilinear Art Nouveau forms. Gaudí devoted his last years to the project, and at the time of his death at age 73 in 1926 less than a quarter of the project was complete. Sagrada Família’s construction progressed slowly, as it relied on private donations and was interrupted by the Spanish Civil War, only to resume intermittent progress in the 1950s.
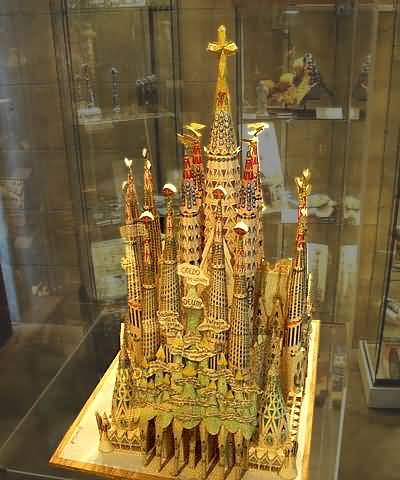

Sagrada Familia Model (Photo Credit: Montrealais / CC BY-SA 3.0)
Construction passed the midpoint in 2010 with some of the project’s greatest challenges remaining and an anticipated completion date of 2026, the centenary of Gaudí’s death. The basílica has a long history of dividing the citizens of Barcelona: over the initial possibility it might compete with Barcelona’s cathedral, over Gaudí’s design itself, over the possibility that work after Gaudí’s death disregarded his design, and the recent proposal to build an underground tunnel of Spain’s high-speed rail link to France which could disturb its stability.
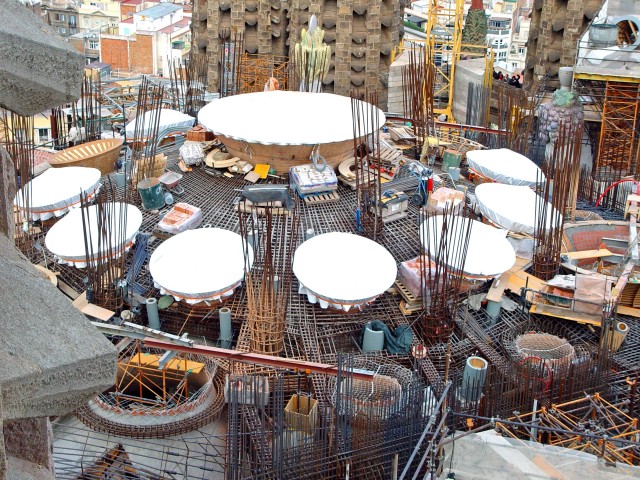

Sagrada Familia Roof (Photo Credit: Etan J. Tal / CC BY 3.0)
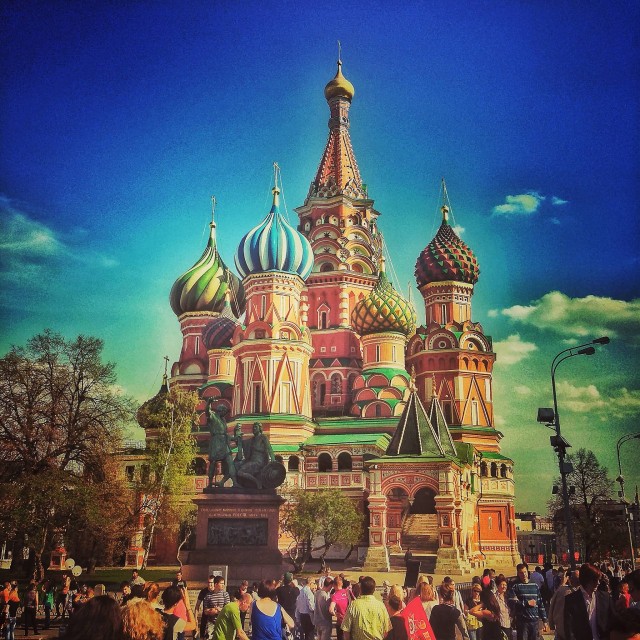
Saint Basil’s Cathedral, Moscow
The Cathedral of Vasily the Blessed, commonly known as Saint Basil’s Cathedral, is a church in Red Square in Moscow, Russia. The building, now a museum, is officially known as the Cathedral of the Intercession of the Most Holy Theotokos on the Moat or Pokrovsky Cathedral.
It was built from 1555–61 on orders from Ivan the Terrible and commemorates the capture of Kazan and Astrakhan. A world famous landmark it was the city’s tallest building until the completion of the Ivan the Great Bell Tower in 1600. The original building, known as Trinity Church and later Trinity Cathedral, contained eight side churches arranged around the ninth, central church of Intercession; the tenth church was erected in 1588 over the grave of venerated local saint Vasily.
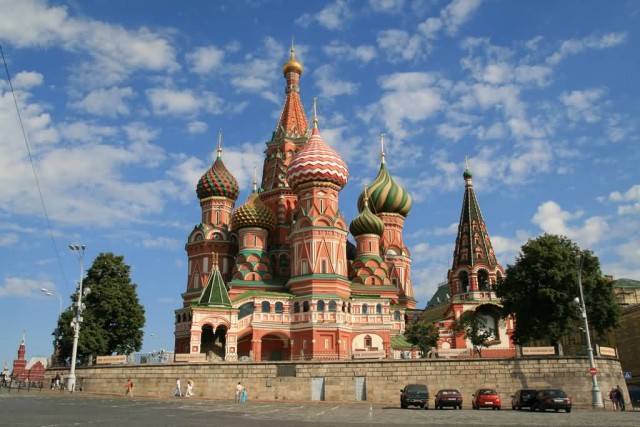

Saint Basil’s Cathedral (Photo Credit: Bernt Rostad / CC BY 2.0)
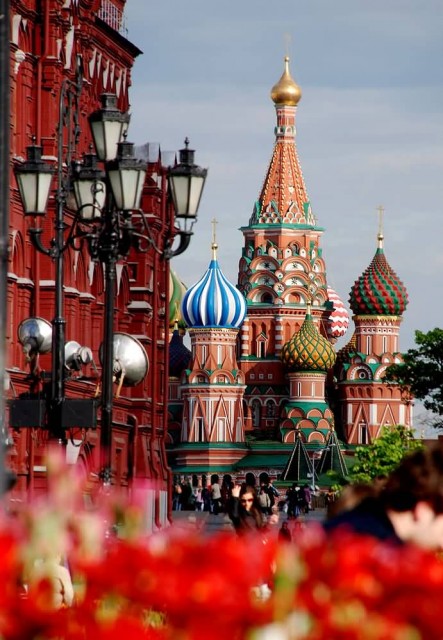

Vasilij Katedralen (Photo Credit: Pål Nordseth / CC BY 2.0)
In the 16th and 17th centuries the church, perceived as the earthly symbol of the Heavenly City, as happens to all churches in Byzantine Christianity, was popularly known as the “Jerusalem” and served as an allegory of the Jerusalem Temple in the annual Palm Sunday parade attended by the Patriarch of Moscow and the tsar.
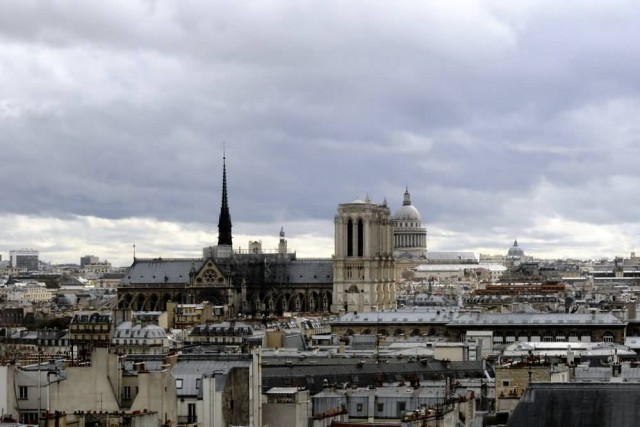
Notre Dame de Paris
Notre-Dame de Paris also known as Notre-Dame Cathedral or simply Notre-Dame, is a historic Catholic cathedral on the eastern half of the Île de la Cité in the fourth arrondissement of Paris, France. The cathedral is widely considered to be one of the finest examples of French Gothic architecture, and it is among the largest and most well-known church buildings in the world.
The naturalism of its sculptures and stained glass are in contrast with earlier Romanesque architecture. As the cathedral of the Archdiocese of Paris, Notre-Dame is the parish that contains the cathedra, or official chair, of the archbishop of Paris, currently Cardinal André Vingt-Trois.

Notre Dame (Photo Credit: Boston Public Library / CC BY 2.0)
The cathedral treasury is notable for its reliquary which houses some of Catholicism’s most important first-class relics including the purported Crown of Thorns, a fragment of the True Cross, and one of the Holy Nails. In the 1790s, Notre-Dame suffered desecration during the radical phase of the French Revolution when much of its religious imagery was damaged or destroyed. An extensive restoration supervised by Eugène Viollet-le-Duc began in 1845. A project of further restoration and maintenance began in 1991.
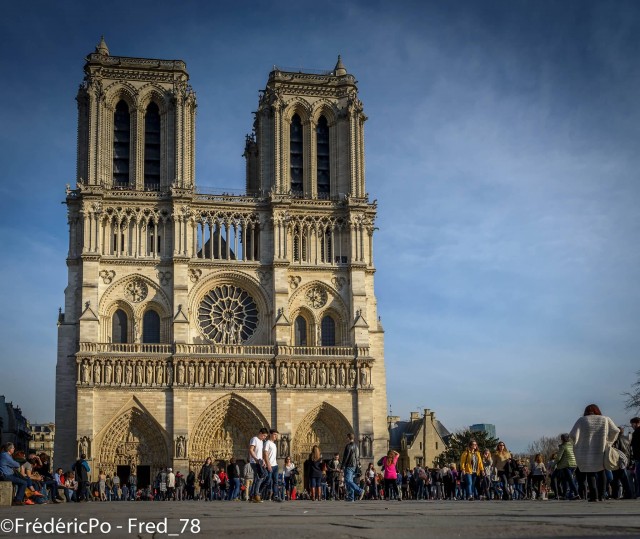

Notre Dame (Photo Credit: Fred PO / CC BY-SA 2.0)
St. Peter’s Basilica, Rome
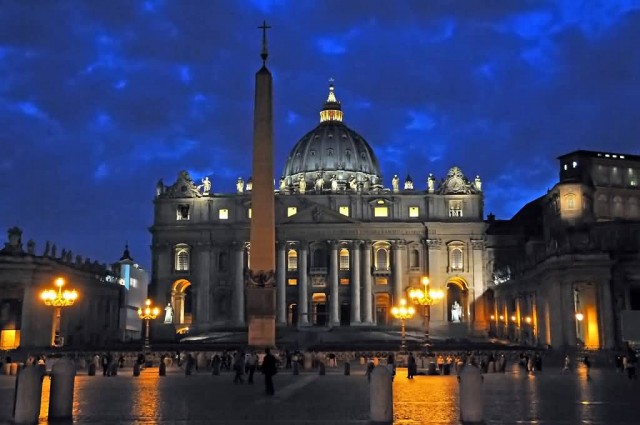

St. Peter S Square (Photo Credit: Dennis Jarvis / CC BY-SA 2.0)
The Papal Basilica of St. Peter in the Vatican, or simply St. Peter’s Basilica is a Late Renaissance church located within Vatican City. Designed principally by Donato Bramante, Michelangelo, Carlo Maderno and Gian Lorenzo Bernini, St. Peter’s is the most renowned work of Renaissance architecture and remains one of the two largest churches in the world. While it is neither the mother church of the Catholic Church nor the Catholic Roman Rite cathedral of the Diocese of Rome, St. Peter’s is regarded as one of the holiest Catholic shrines. It has been described as “holding a unique position in the Christian world” and as “the greatest of all churches of Christendom”.
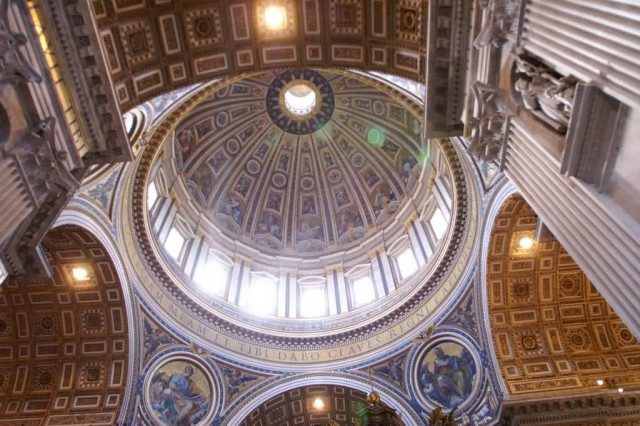

The Dome Of St. Peter’s (Photo Credit: David Merrett / CC BY 2.0)
By Catholic Tradition, the Basilica is the burial site of its namesake St. Peter, one of the Apostles of Jesus Christ and, also according to Tradition, the first Pope and Bishop of Rome. Tradition and strong historical evidence hold that St. Peter’s tomb is directly below the high altar of the Basilica. For this reason, many Popes have been interred at St. Peter’s since the Early Christian period. There has been a church on this site since the time of the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great. Construction of the present basilica, replacing the Old St. Peter’s Basilica of the 4th century AD, began on 18 April 1506 and was completed on 18 November 1626.
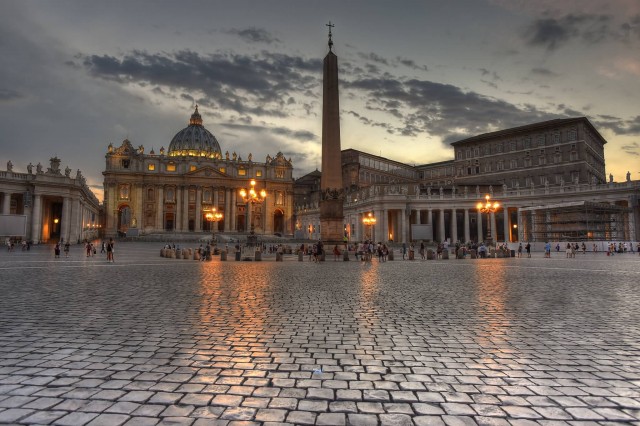

The Lights Come On After Sunset At St. Peter’s Basilica (Photo Credit: Diana Robinson / CC BY 2.0)
Westminster Abbey, London

Westminster Abbey (Photo Credit: Nathanael Burton / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of St Peter at Westminster, is a large, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, located just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the most notable religious buildings in the United Kingdom and has been the traditional place of coronation and burial site for English and, later, British monarchs. Between 1540 and 1556 the abbey had the status of a cathedral.
Since 1560, however, the building is no longer an abbey nor a cathedral, having instead the status of a “Royal Peculiar” – a church responsible directly to the Sovereign. According to a tradition first reported by Sulcard in about 1080, a church was founded at the site in the 7th century, at the time of Mellitus, a Bishop of London. Construction of the present church began in 1245, on the orders of Henry III.
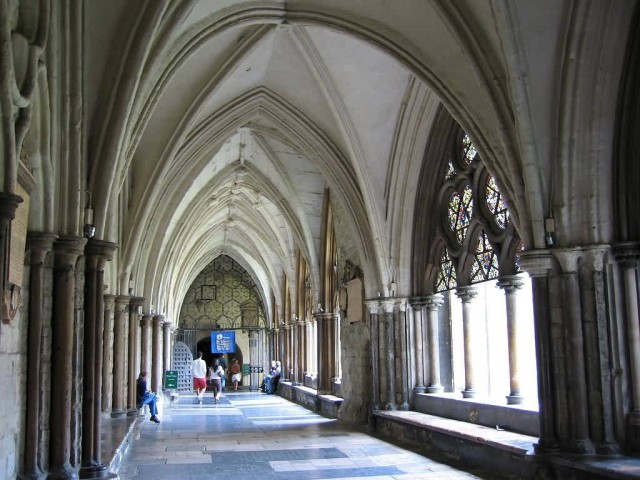

The Cloisters Westminster Abbey (Photo Credit: Marty B / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Since 1066, when Harold Godwinson and William the Conqueror were crowned, the coronations of English and British monarchs have been held here. Since 1100, there have been at least 16 royal weddings at the abbey. Two were of reigning monarchs, although before 1919 there had been none for some 500 years.

Westminster Abbey Royal Wedding (Photo Credit: Gareth Williams / CC BY 2.0)
St Paul’s Cathedral, London
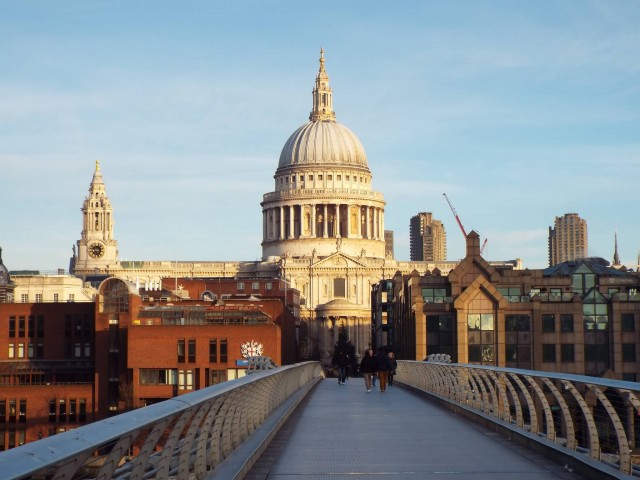

St. Paul’s Cathedral (Photo Credit: Matt Smith / CC BY-SA 2.0)
St Paul’s Cathedral, London, is an Anglican cathedral, the seat of the Bishop of London and the mother church of the Diocese of London. It sits at the top of Ludgate Hill, the highest point in the City of London. Its dedication to Paul the Apostle dates back to the original church on this site, founded in AD 604.
The present church, dating from the late 17th century, was designed in the English Baroque style by Sir Christopher Wren. Its construction, completed within Wren’s lifetime, was part of a major rebuilding programme which took place in the city after the Great Fire of London. St Paul’s Cathedral occupies a significant place in the national identity of the English population. It is the central subject of much promotional material, as well as postcard images of the dome standing tall, surrounded by the smoke and fire of the Blitz.
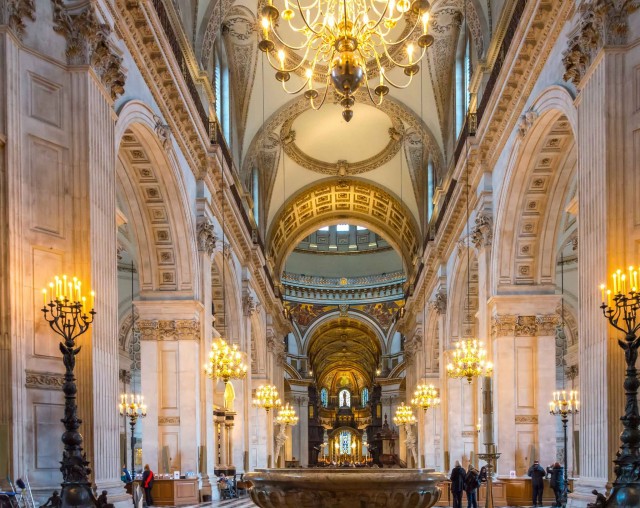

St Paul’s Cathedral (Photo Credit: JackPeasePhotography / CC BY 2.0)
Important services held at St Paul’s have included the funerals of Lord Nelson, the Duke of Wellington, Sir Winston Churchill and Margaret Thatcher; Jubilee celebrations for Queen Victoria; peace services marking the end of the First and Second World Wars; the wedding of Charles, Prince of Wales, and Lady Diana Spencer, the launch of the Festival of Britain and the thanksgiving services for the Golden Jubilee, the 80th Birthday and the Diamond Jubilee of Elizabeth II. St Paul’s Cathedral is a busy working church, with hourly prayer and daily services.
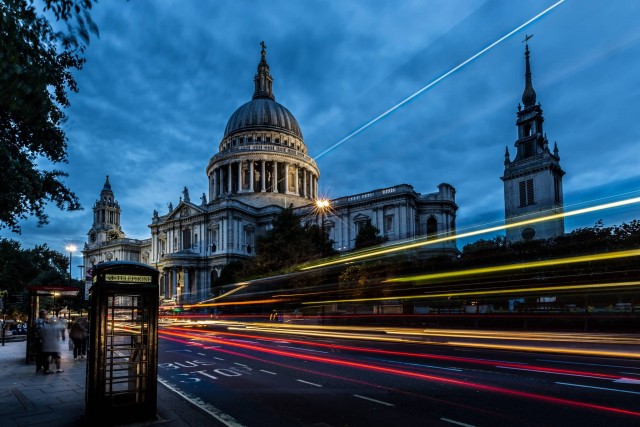

St. Paul’s Cathedral (Photo Credit: Davide D’Amico / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Church of the Nativity, Bethlehem
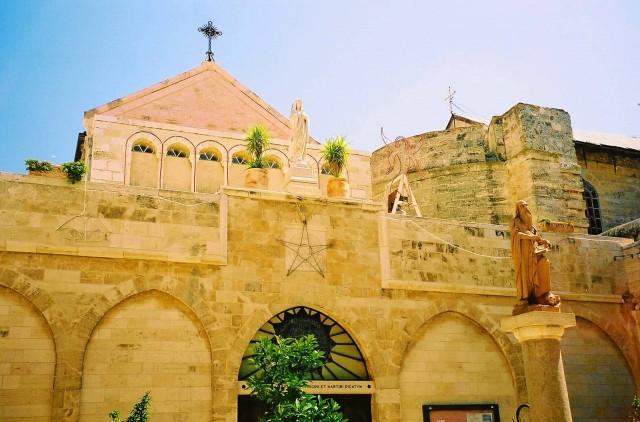

Church Of The Nativity (Photo Credit: AUTHORNAME / CC BY 2.0)
The Church of the Nativity is a basilica located in Bethlehem, Palestine. The church was originally commissioned in 327 AD by Constantine and his mother Helena over the site that is still traditionally considered to be located over the cave that marks the birthplace of Jesus of Nazareth. The Church of the Nativity site’s original basilica was completed in 339 AD and destroyed by fire during the Samaritan Revolts in the sixth century AD.
A new basilica was built 565 AD by Justinian, the Byzantine Emperor, restoring the architectural tone of the original. The site of the Church of the Nativity has had numerous additions since this second construction, including its prominent bell towers.
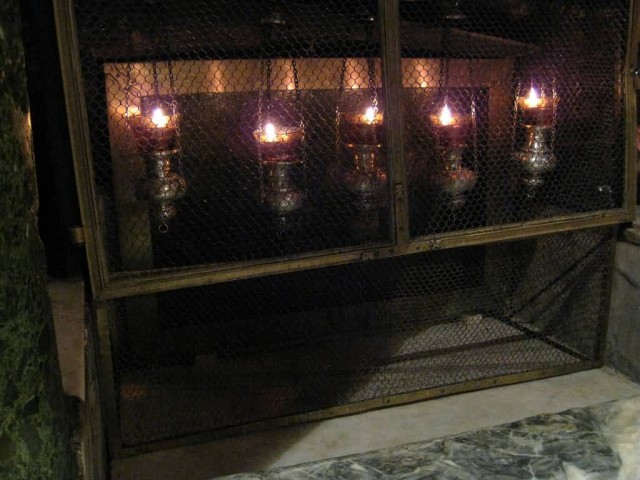

Grotto Of The Nativity (Photo Credit: Chris Yunker / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Due to its cultural and geographical history, the site holds a prominent religious significance to those of both the Christian and Muslim faiths. The site of the Church of the Nativity is a World Heritage Site, and was the first to be listed under Palestine by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. The site is also on UNESCO’s List of World Heritage Sites in Danger.

Church Of The Nativity (Photo Credit: Chris Yunker / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Church of the Holy Sepulchre, Jerusalem
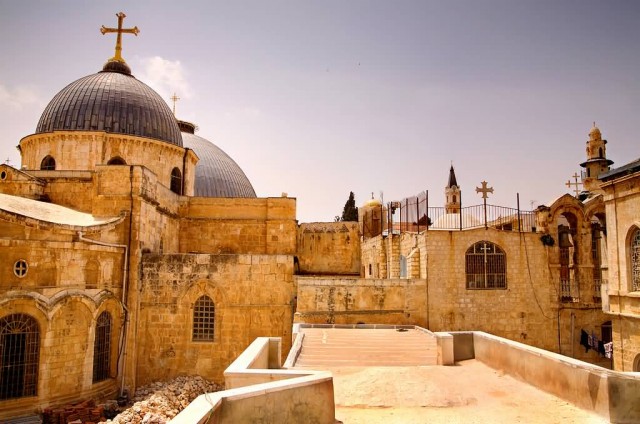

Church Of The Holy Sepulchre (Photo Credit: AUTHORNAME / CC BY-SA 2.0)
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre also called the Church of the Resurrection by Orthodox Christians is a church within the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. It is a few steps away from the Muristan. The site is venerated as Calvary where Jesus of Nazareth was crucified, and also contains the place where Jesus is said to have been buried and resurrected. Within the church are the last four Stations of the Cross along the Via Dolorosa, representing the final episodes of Jesus’ Passion.
The church has been an important Christian pilgrimage destination since at least the fourth century as the traditional site of the resurrection of Christ. Today it also serves as the headquarters of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem, while control of the building is shared between several Christian churches and secular entities in complicated arrangements essentially unchanged for centuries.
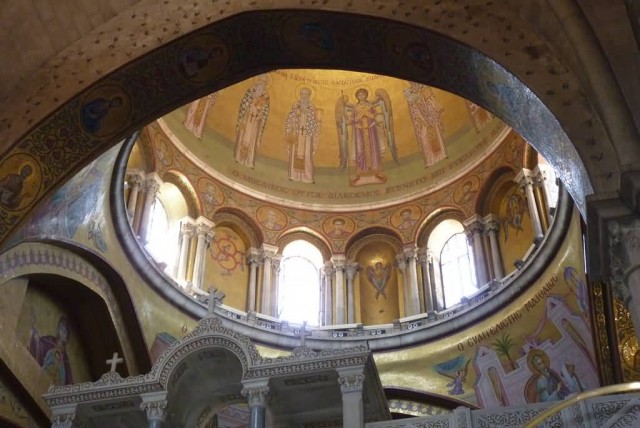

Inner Curve Of The Church (Photo Credit: AUTHORNAME / CC BY 2.0)
Today, the church is home to branches of Eastern Orthodoxy and Oriental Orthodoxy as well as to Roman Catholicism. Anglicans and Protestants have no permanent presence in the Church and some have regarded the Garden Tomb, elsewhere in Jerusalem, as the true place of Jesus’ crucifixion and resurrection.
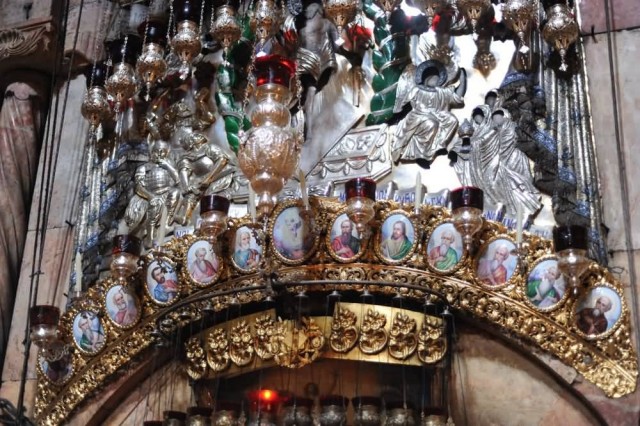

Entry Of The Aedicule (Photo Credit: Guillaume Paumier / CC BY 2.0)
Saint Mark’s Basilica, Venice
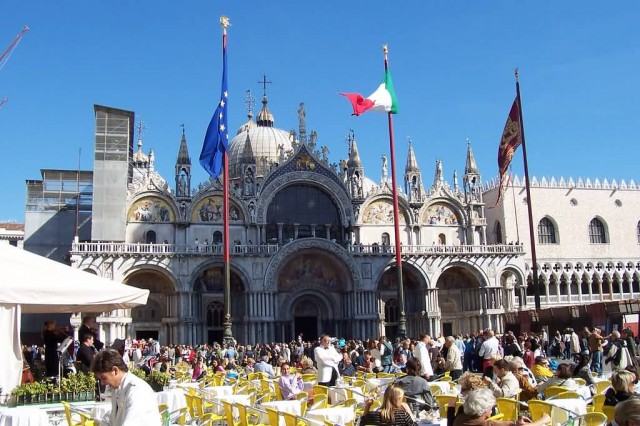

Basilica San Marco Venice Italy (Photo Credit: Neil Willsey / CC BY-SA 2.0)
The Patriarchal Cathedral Basilica of Saint Mark is the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Venice, northern Italy. It is the most famous of the city’s churches and one of the best known examples of Italo-Byzantine architecture. It lies at the eastern end of the Piazza San Marco, adjacent and connected to the Doge’s Palace.
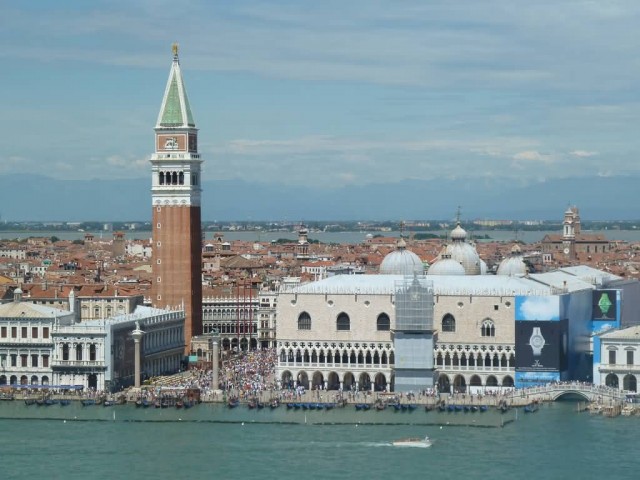

View Of Saint Mark’s Square Maggiore (Photo Credit: Alistair Young / CC BY 2.0)
Originally it was the chapel of the Doge, and has only been the city’s cathedral since 1807, when it became the seat of the Patriarch of Venice, archbishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Venice, formerly at San Pietro di Castello. For its opulent design, gold ground mosaics, and its status as a symbol of Venetian wealth and power, from the 11th century on the building has been known by the nickname Chiesa d’Oro.
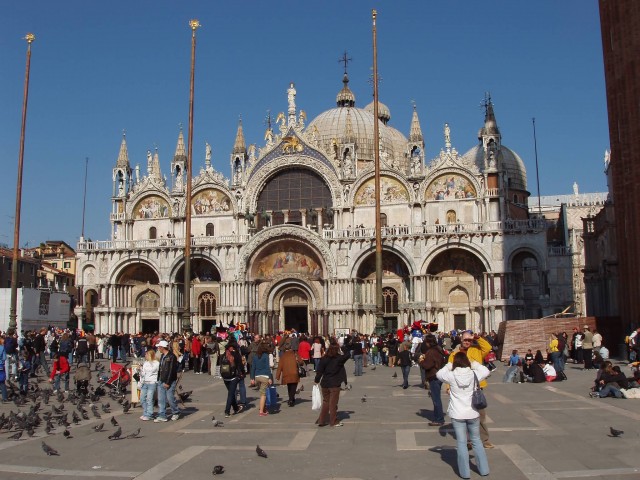

Venice Saint Mark’s Basilica (Photo Credit: Mark Huguet / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Hagia Sophia, Istanbul
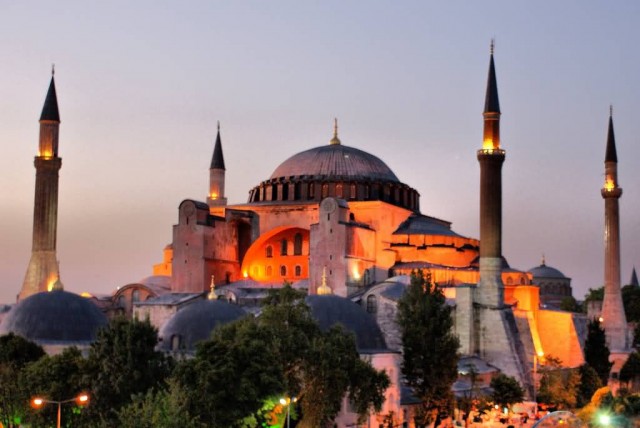

Hagia Sophia Istanbul At Dusk (Photo Credit: David Spender / CC BY 2.0)
Hagia Sophia is a former Greek Orthodox patriarchal basilica, later an imperial mosque, and now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey. From the date of its construction in 537 until 1453, it served as an Eastern Orthodox cathedral and seat of the Patriarchate of Constantinople, except between 1204 and 1261, when it was converted to a Roman Catholic cathedral under the Latin Empire.
The building was a mosque from 29 May 1453 until 1931. It was then secularized and opened as a museum on 1 February 1935. The church was dedicated to the Wisdom of God, the Logos, the second person of the Holy Trinity, its patronal feast taking place on 25 December, the commemoration of the birth of the incarnation of the Logos in Christ. Although sometimes referred to as Sancta Sophia, sophia being the phonetic spelling in Latin of the Greek word for wisdom, “Shrine of the Holy Wisdom of God”.
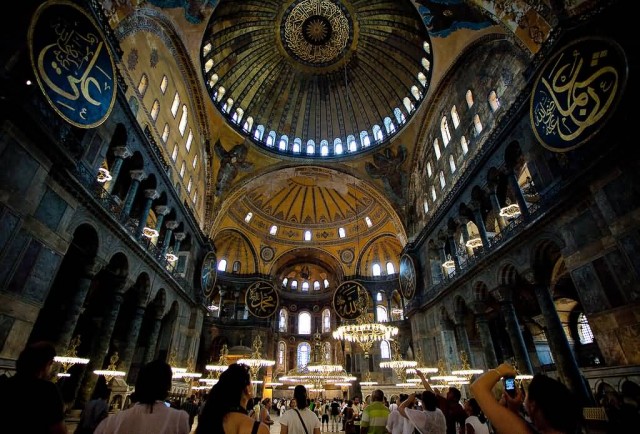

Hagia Sophia Istanbul (Photo Credit: Esther Lee / CC BY 2.0)
The church contained a large collection of holy relics and featured, among other things, a 15-m silver iconostasis. The focal point of the Eastern Orthodox Church for nearly one thousand years, the building witnessed the excommunication of Patriarch Michael I Cerularius on the part of Pope Leo IX in 1054, an act which is commonly considered the start of the Great Schism. From its initial conversion until the construction of the nearby larger Sultan Ahmed Mosque in 1616, it was the principal mosque of Istanbul. The Hagia Sophia served as inspiration for many other Ottoman mosques, such as the Blue Mosque, the Şehzade Mosque, the Süleymaniye Mosque, the Rüstem Pasha Mosque and the Kılıç Ali Paşa Mosque.
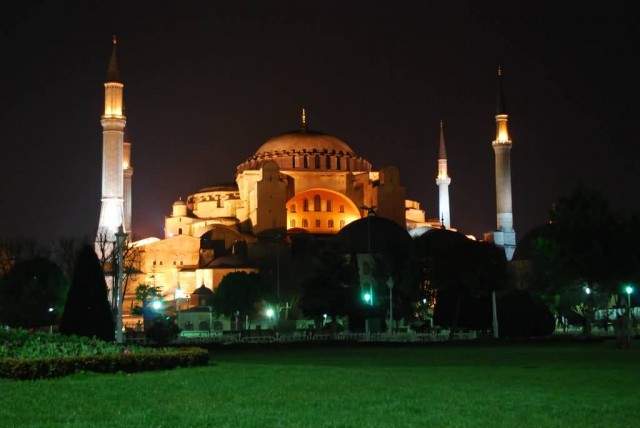

Hagia Sophia At Night (Photo Credit: Ivan Mlinaric / CC BY 2.0)