Top 5 Longest Mountain Ranges On Earth

View From The Highest Point (Photo Credit: Torrenegra / CC BY 2.0)
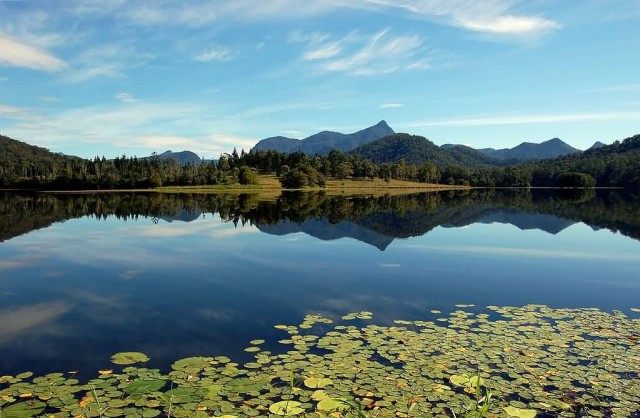
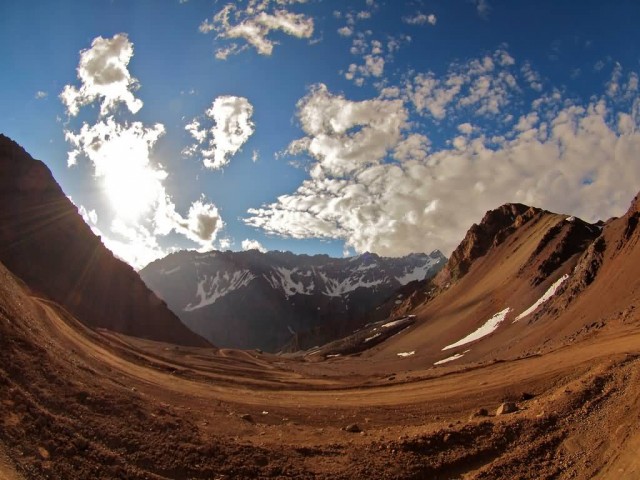
Andes
The Andes is the longest continental mountain range in the world. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about 7,000 km long, about 200 km to 700 km wide and of an average height of about 4,000 m. The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina.
The Andes can be divided into three sections:
- The Southern Andes (south of Llullaillaco) in Argentina and Chile;
- The Central Andes in Ecuador, Peru and Bolivia
- The Northern Andes (north of the Nudo de Pasto) in Venezuela and Colombia which consist of three parallel ranges, the western, central, and eastern ranges.

Andes Mountains (Photo Credit: Avraham Elias / CC BY 2.0)
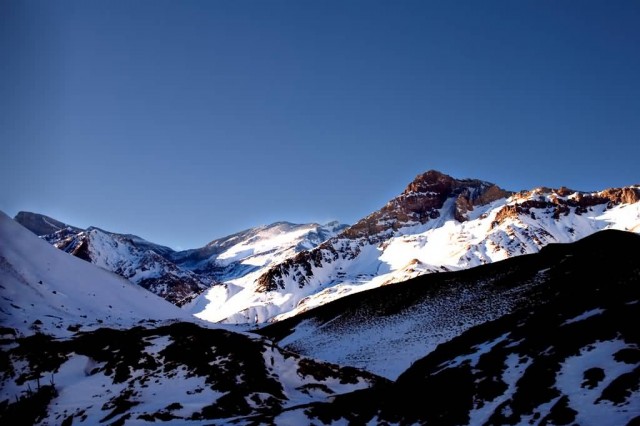
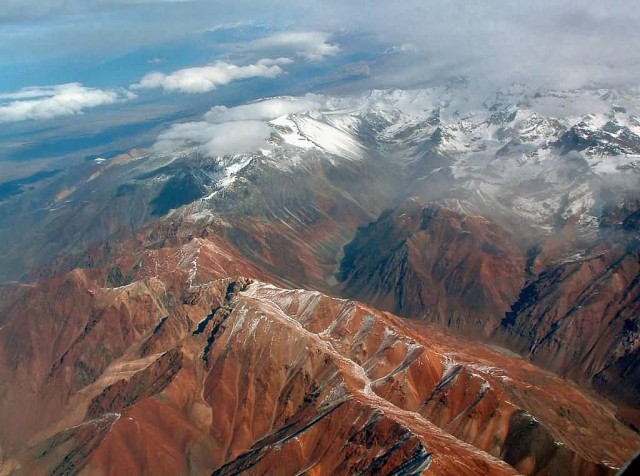
The Andes range has many active volcanoes, which are distributed in four volcanic zones separated by areas of inactivity. Temperature, atmospheric pressure and humidity decrease in higher elevations. The southern section is rainy and cool, the central section is dry. The northern Andes is typically rainy and warm, with an average temperature of 18 °C in Colombia. The climate is known to change drastically in rather short distances.he Andes is rich in fauna: With almost 3,500 species, of which roughly 2/3 are endemic to the region, the Andes is the most important region in the world for amphibians.

Andes (Photo Credit: Robert Morrow / CC BY-SA 3.0)
Rocky Mountains
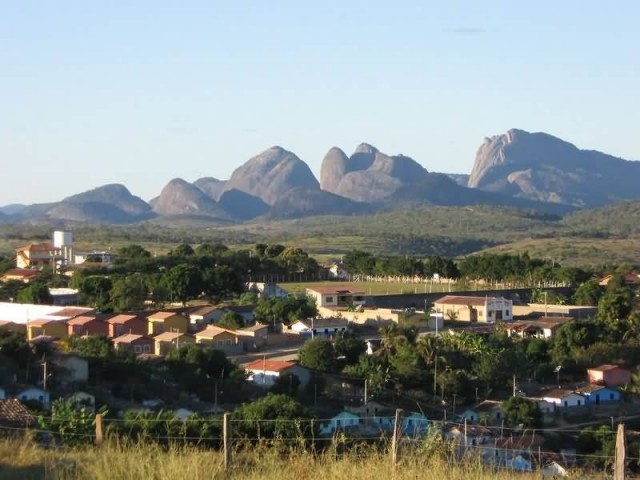

Rocky Mountains (Photo Credit: Deborahdutra / CC BY-SA 3.0)
Rocky Mountains, commonly known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than 3,000 miles from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States. There are a wide range of environmental factors in the Rocky Mountains. Since the last great ice age, the Rocky Mountains were home first to indigenous peoples including the Apache, Arapaho, Bannock, Blackfoot, Cheyenne, Crow Nation, Flathead, Shoshone, Sioux, Ute, Kutenai, Sekani, Dunne-za and others.

Rocky Mountains (Photo Credit: T.Voekler / CC BY-SA 3.0)
Economic resources of the Rocky Mountains are varied and abundant. Minerals found in the Rocky Mountains include significant deposits of copper, gold, lead, molybdenum, silver, tungsten, and zinc. Every year the scenic areas and recreational opportunities of the Rocky Mountains draw millions of tourists. The main language o the Rocky Mountains is English. But there are also linguistic pockets of Spanish and indigenous languages. French is another official language in Canada’s national parks.

Rocky Mountains (Photo Credit: Shawn / CC BY-SA 2.0)
Himalayas
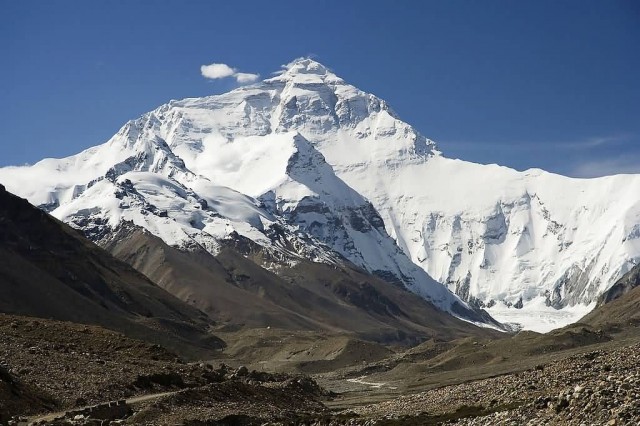

Himalayas Everest (Photo Credit: Lucag / CC BY-SA 3.0)
The Himalayas, or Himalaya, literally meaning “abode of snow” is a mountain range in South Asia which separates the Indo-Gangetic Plain from the Tibetan Plateau. This range is home to nine of the ten highest peaks on Earth, including the highest, Mount Everest. The Himalayas have profoundly shaped the cultures of South Asia. Many Himalayan peaks are sacred in both Buddhism and Hinduism.
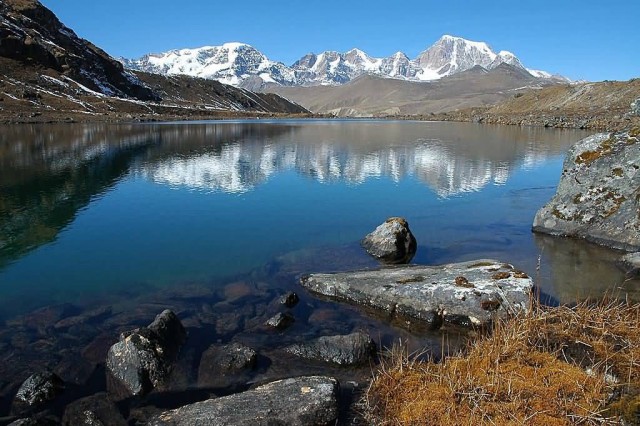

Crows Lake In North (Photo Credit: Lucag / CC BY-SA 3.0)
The Himalayas have the third largest deposit of ice and snow in the world, after Antarctica and the Arctic lakes include She-Phoksundo Lake in the Shey Phoksundo National Park of Nepal, Gurudongmar Lake, in North Sikkim, Gokyo Lakes in Solukhumbu district of Nepal and Lake Tsongmo, near the Indo-China border in Sikkim. The Himalayas have a profound effect on the climate of the Indian subcontinent and the Tibetan Plateau. They prevent frigid, dry winds from blowing south into the subcontinent, which keeps South Asia much warmer than corresponding temperate regions in the other continents.
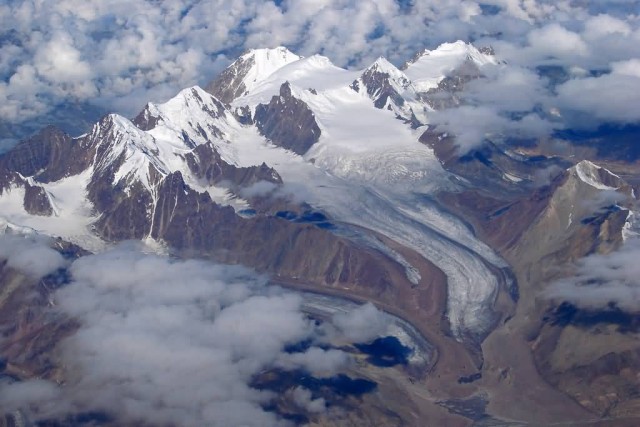

The Great Himalayas (Photo Credit: Karunakar Rayker / CC BY 2.0)
Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, or the Eastern Highlands, is Australia’s most substantial mountain range and the third longest land-based range in the world. The Great Dividing Range was formed during the Carboniferous period. The range stretches more than 3,500 kilometres from Dauan Island off the northeastern tip of Queensland, running the entire length of the eastern coastline through New South Wales, then into Victoria and turning west, before finally fading into the central plain at the Grampians in western Victoria.
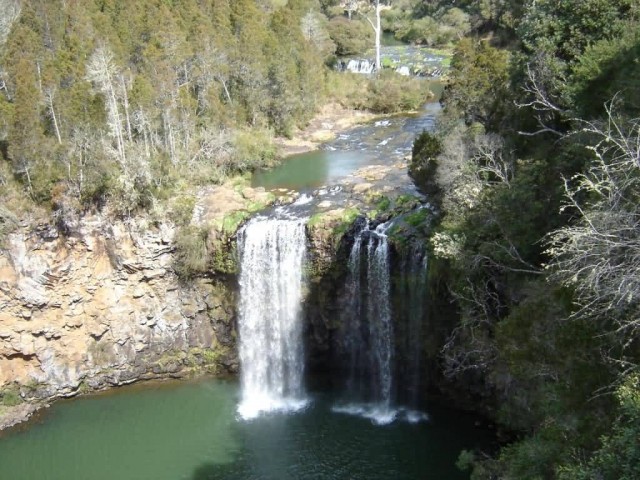

Dangar Falls Dorrigo (Photo Credit: Ajayvius / Public Domain)
The width of the range varies from about 160 km to over 300 km. At some high hill passes the range provides cool sites appropriate for vineyards. The ranges is also the source of virtually all of eastern Australia’s water supply, both through runoff caught in dams and throughout much of Queensland, through the Great Artesian Basin. Some of the rivers which flow west of the ranges includes the Condamine River, Flinders River, Herbert River, Lachlan River, Macdonald River, Macintyre River and Namoi River.
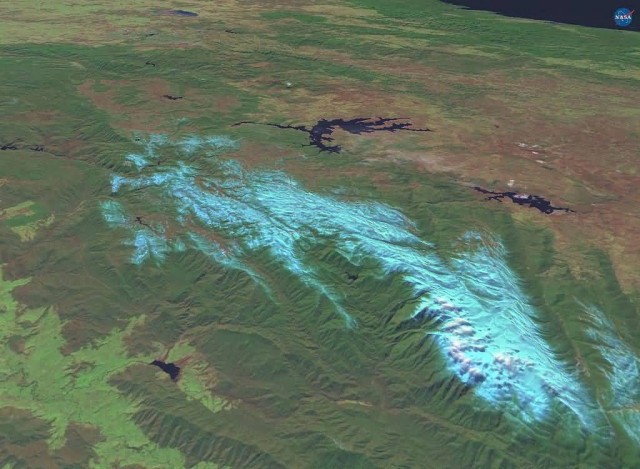
Worldwind Snowy Mountains (Photo Credit: Chuq / Public Domain)
Trans-Antarctic Mountains
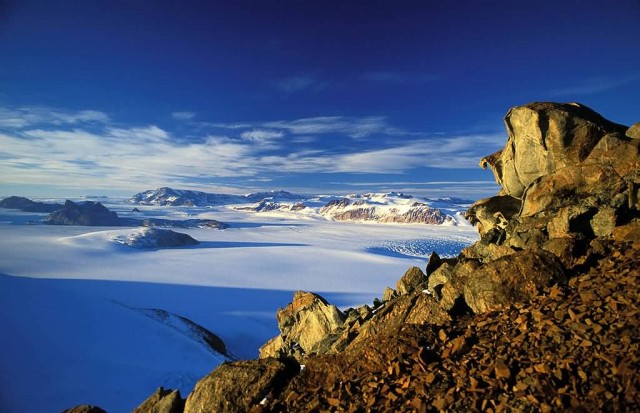

Trans-Antarctic Mountains (Photo Credit: Hannes Grobe / CC BY-SA 2.5)
The Transantarctic Mountains comprise a mountain range in Antarctica which extend, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria Land to Coats Land. These mountains divide East Antarctica and West Antarctica. They include a number of separately named mountain groups, which are often again subdivided into smaller ranges.
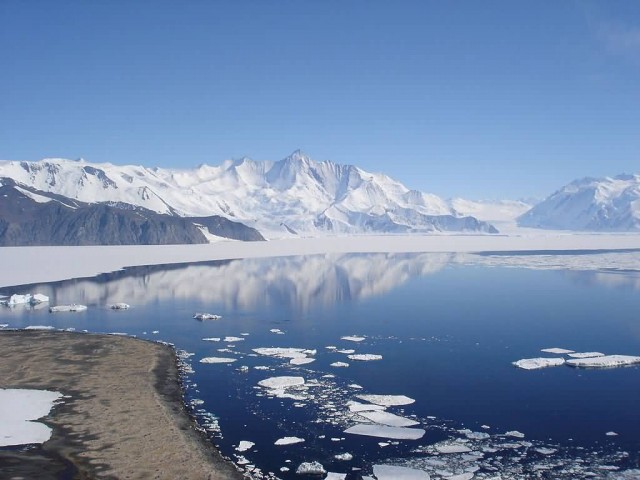

Trans-Antarctic Mountains (Photo Credit: Andrew Mandemaker / CC BY-SA 2.5)
The mountain range stretches between the Ross Sea and the Weddell Sea the entire length of Antarctica, hence the name. With a total length of about 3,500 km, the Transantarctic Mountains are one of the longest mountain ranges on Earth in the early Cenozoic. The mountains consist of sedimentary layers lying upon a basement of granites and gneisses. The sedimentary layers include the Beacon Supergroup sandstones, siltstones, and coal deposited beginning in the Silurian period and continuing into the Jurassic.
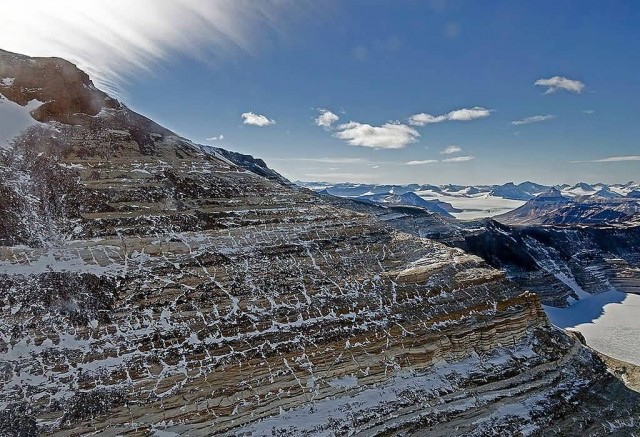

View Of The Trans-Antarctic Mountains (Photo Credit: NASA / Michael Studinger/ Public Domain)
















